With funding provided by a grant from the US Department of Education, I was able to design a course for the San Diego State University Center for (now Department of) Asian Studies.1 Initially the course, East Asian Philosophies: Logic and Language, focused on China, Korea, and Japan. A textbook of primary and secondary readings was compiled, to which I added an introduction and background materials. Subsequently, both the course contents and the text were expanded to include India, Tibet, and Vietnam, as well as Mahayana Buddhism. The revised course title, Asian Philosophies: Logic, Language, and Aesthetics, reflects this expansion.
The key role played by the arts in Asia as the connecting link between logic and language became increasingly apparent as I taught the class. The arts, in various manifestations, reflect cultural assumptions about order inherent in forms of logic, language, and philosophy. Accordingly, each chapter of the text provides a discussion of the aesthetics underlying the culture or topic addressed. A contemporary connection was forged through discussions of science, the primary arbiter of order in today’s world, and the scientist’s obsession with beauty.2
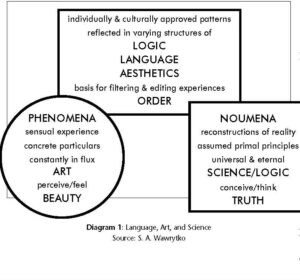
This approach proved to be an ideal point of entry into the often mystifying world of Asian philosophy for students with limited exposure to Asian culture. Aesthetics, derived from the Greek aisthetikos (sensory, sensitive), involves the ability to perceive, be sensitive to, cosmic (from the Greek kosmos, order, harmony) patterns prior to processing them through human thought. If beauty is in the eye of the beholder, may it not equally be the case that logic is in the mind of the thinker? Thus aesthetic theories are infused with cultural conceptions of order, whether expressed as beauty, harmony, or goodness (see diagram 1). The prominent role of Nature in Asian aesthetic principles must be especially recognized and appreciated.
I must hasten to add, however, that the following discussion in no way encourages or supports a simplistic, reductionist reading of either Asian or non-Asian culture. It is not my intention to suggest that the artistic expressions dealt with here represent an encapsulation of aesthetics “East” and “West.” Following the lead of Hajime Nakamura (Ways of Thinking of Eastern Peoples), I reject the stereotypical East/West dichotomy of values, as well as the assumption that any culture can be readily subsumed under a single principle.
To open the minds of students to the broad horizons of Asian philosophy, a cross-cultural, multi-media excursion encompassing alternative forms of architecture, garden design, musical composition, and performance was provided. Japan’s Katsura Imperial Villa was chosen as an extreme manifestation of the Zen aesthetic, while the Palace of Versailles embodied an equally extremist view of “western” tastes. Although both were constructed during the same general time period, the seventeenth century, and were the pet projects of royalty, the results are strikingly different in terms of design and interaction with the natural environment, a difference reflective of vastly diverse assumptions concerning aesthetics, logic, and order. Each stands as a unique testimony to a very specific conception and expression of aesthetics possessed by the equally unique personalities involved in their construction.
Students were given a vicarious experience of each site. They then were asked to evaluate 1) the conceptions evoked by maps of the sites, as well as 2) their perceptions of video tours and accompanying musical selections. After analyzing their experiences, they attempted to synthesize the defining principles of each site guided by the following questions:
How are the sites planned and ordered?
What is revealed about respective definitions of beauty and order?
How does the music mirror the physical environment?
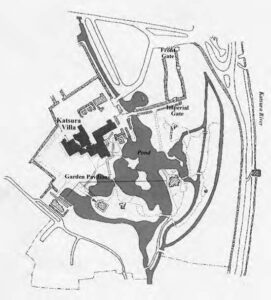
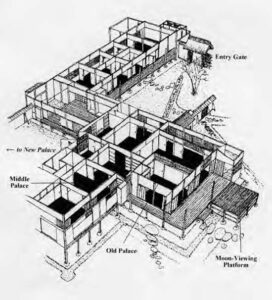
The amorphous layout of Katsura (fig. 1) and the simple elegance of its buildings (fig. 2) contrast sharply with the geometrical precision and intricacies of Versailles (fig. 3), distinguished by its grandiose multi-storied facades. Design with Nature is evident in the former site, just as the latter demonstrates the imposition of rigorous control to “improve” Nature in line with human desires.
The comparative experience evoked a variety of responses. One student succinctly noted the incongruities between these contemporaneous art forms: from Versailles he concluded “one needs to be powerful to waste resources,” while Katsura was viewed as being “without much detail.” Similarly, the Japanese music selection undulates sensuously, punctuated by silences; the French composition reflects the mathematical patterns beloved by Baroque tastes. After discussing student reactions, we began to delve into the specifics of each site, seeking to uncover the underlying cultural assumptions responsible for the huge artistic differences. What follows are some points of comparison—the what, who, how, why of architecture and garden design as well as musical composition and performance, along with comments on the respective ambiance and underlying aesthetic/philosophical/cultural principles of the designs.
Source: http://www.getty.edu/artsednet/images/BM/Katsura/cross.html
Again, it is important to note that a multitude of styles are to be found among Asian cultures and within individual cultures over time, just as the symmetrical design principles characteristic of Versailles are not the exclusive choice of the West. Sites in India (the Taj Mahal), China (the Forbidden City), Cambodia (Angkor Wat), and even Japan (Todai-ji) can readily be identified that reflect a preference for rigidly balanced, ostentatious, and extravagant designs. Similarly, an appreciation for naturalness and simplicity is not unknown in non-Asian cultures. The same diversity of tastes can be found in musical expression.

Source: http://www.lenotre.culture.gouv.fr/culture/celebrations/lenotre/en/ja/index.htm
The above introductory glimpse of extreme aesthetic possibilities laid the ground for subsequent discussions of Asian logic, language, and aesthetics. We went on to explore eight themes/chapters outlining the richness of Asian thought and culture, beginning with India. This seemed a natural progression, given India’s link to European culture through examples of shared membership in the Indo-European language family, including Sanskrit, Pali, Hindi, Punjabi, Nepali, etc. A family resemblance also can be discerned between ancient Greek and Vedic assumptions concerning phenomena and noumena, body and mind, desire and reason. Discussions of beauty (rasa) highlighting the roles of emotion and physicality were balanced by epistemological excursions into early Buddhism and the Ny¯aya logic of later Hinduism. These allowed for interesting comparisons with ancient Greek views of the same topics. We concluded this section with a provocative piece from twentieth century philosopher Krishnamurti, “What is Thinking?”
This prepared the way for more challenging presentations of Indian and Central Asian Mahayana Buddhism—The Lioness Roar of Queen Srimala expounding the seminal Tathagata (Suchness) concept, Nagarjuna’s Madhyamika logic (Middle Path Between Affirming and Denying), and the Lotus Sutra. Vajrayana Buddhism, the Diamond or Thunderbolt Vehicle, was explored within the Tibetan cultural context, including a sophisticated ritual symbolism steeped in the arts while informed by Tibetan Buddhist psychology. These insights were supported by philosophical contributions from both traditional philosophers, such as Milarepa, and contemporary proponents Chogyam Trungpa and the current Dalai Lama.
Moving on to East Asia, individual chapters were devoted to China and Japan, as well as the less often explored areas of Korea and Vietnam. Again, cultural contexts for their respective aesthetics were provided, then further expanded through philosophical discussions past and present. Thus the Chinese worldview was introduced through the fundamental Yin/Yang principles of the Yi Jing, then elaborated in the varying views of Xun Zi’s humanistic Confucian logic, Zhuang Zi’s Daoist critique of logic and language, and a contemporary Chan Master. The Korean cultural aesthetics of mot (utter naturalness) was followed by excerpts from Buddhist Masters Chinul and T’aego. Vietnamese poetry represented the confluence of aesthetics and Buddhist philosophy, also reflected in Thich Nhat Hanh’s profound yet unassuming teaching on interdependence in “The Almond Tree in Your Front Yard.” The primal “ah-ness” of Japan’s mono no aware aesthetic provided the prelude to Kukai’s philosophically-infused Tantric poetry and Dogen’s Soto Zen, expressed both poetically and in the essay format of the Shobo-genzo.
The concluding chapter considered the connections between Asian logics and post-modern science, inclusive of Fuzzy Logic and Chaos Theory. Western scientists have been at the forefront of research linking ancient Asian traditions with the New Physics. The underlying insight here is that the mechanistic model of the universe assumed by Newtonian physics fails to account for the complexity of the workings of the universe, whether manifested in the formation of a distant galaxy or the rhythms of the human heart. The order sought by science in the past is in many ways deficient, an enforced Procrustean fit that fails to illuminate the full range of reality. In seeking philosophies conversant with the fact of change we find promising candidates in the Yin/Yang complementarities of the Yi Jing, or Buddhism’s sophisticated analyses of Interdependent Origination (Pratitya-samutpada). Provocative questions arose:
Is logic one or many?
Can a science be founded on chaos?
Does order exist merely in the mind of the beholder?
If so, can the same be said for chaos?
What are limits of both logic and science in the broadest possible cross-cultural senses?
What might be learned by opening our awareness to other voices, other languages, other logics?
Each art form, aesthetic theory, and philosophical expression contains its own logic, encapsulating a language of the culture from which it originated. By deconstructing stereotypes of Asian art through an initial comparison with European examples from the same time period (Katsura versus Versailles), students were able to “empty their teacups” vis-à-vis Asian culture. This fresh perspective made them more receptive to the task of judging Asian philosophers on their own cultural terms, while seeking philosophical wisdom that transcends all cultures.
East/West Aesthetics: Architecture and Garden Design
Katsura Imperial Villa
WHAT
- Cottage/tea house transformed into imperial villa with Zen tea garden
- 6 acres (6.5 hectares)
- Wood bark roof, lack of sculptures or brightly colored paintings in interiors, mainly single story structures, large meandering pond, five tea huts
WHO
- Father and son, Prince Toshihito (1579–1629) and Prince Toshitada (1616–1662) of the Hachijo family
HOW
- Designed by the Hachijo princes themselves, lovingly constructed using the description of a garden in The Tale of Genji:
—“The garden was designed not only to be viewed from the buildings, but was also a large-scale tea garden. Its pathway was deliberately designed to provide viewers with a variety of views throughout the garden. Its pathway was particularly planned for the purpose of moon viewing and appreciation of the natural beauty of the four seasons.”3 - The princes’ limited financial resources were carefully controlled to insure consummate craftsmanship
WHY
- Inspired by the Heian aesthetic and its primary literary product, Murasaki Shikibu’s Tale of Genji; a villa near the Katsura site inspired Murasaki’s fictional estate for Genji
- parallels between the respective political disappointments of the fictional Prince Genji and Prince Toshihito
- Katsura, “a much desired yet unattainable goal”
- recurring moon symbolism (where the Katsura tree grows)4 and flower viewing (seasonal cycle)
- inspiration for poetic composition, tea ceremony, active participation in creativity
- —“the architecture and the garden become occasions for spiritual elevation. . . . the garden . . . is meant to be a place where the viewer can become aware of his existence as part of nature” leaving behind “political misfortunes.”5
- —“it was built so that walkers may feel something of Zen”6
AMBIANCE
- Nature-oriented; shifting, muted shadows
- —“a completely isolated miracle in the civilized world”7
- —“Here spirit is tempered over matter, greatness of conception is expressed by utter simplicity, the tangible by the intangible.”8
- —“Nothingness is truly well expressed here. Also present is a genuine Naturalness, for we feel nothing unnatural or artificial.”9
UNDERLYING PRINCIPLES
- Aged appearance, rounded shapes
- Asymmetry, austerity (“Lofty Dryness”), profound subtlety (“Deep Reserve”), simplicity, naturalness, non-attachment, tranquillity10
—“here we feel in the presence of No Mind, of an unintentional quality that is artless and natural, the kind of Naturalness beyond mere naturalness, made by man but nevertheless truly natural and far from any element of exertion.”11
The Palace of Versailles
WHAT
- Hunting lodge transformed into palatial principal residence with formal gardens
- Nearly 15,000 acres in its original form surrounded by 27 miles of wall
- Endless corridors of extravagantly embellished rooms, grounds featuring pools, statues, fountains, groves, stables, and flowerbeds, all meticulously maintained
WHO
- Father and son, Louis XIII (1601–1643) and Louis the XIV (1638–1715) (“L’etat, c’est moi” [I am the state])
HOW
- Garden design by André Le Nôtre (1613–1700), educated in mathematics, geometry, architecture, painting, who “cared not for money but only for beauty. . . . [he] resolved to turn the ‘disorder’ of nature into order, harmony and reasonable, intelligible form.”12
Chief architect Jules Hardouin-Mansart (1646–1708), exponent of French Baroque classicism - An unlimited budget that burdened the people has been compared to the current cost of a modern airport or an aircraft carrier, estimated by Will and Ariel Durant at $500,000,000
WHY
- Venue for glorifying the gods of Olympus and pagan revelries
- lavish theatrical entertainments reflecting the power and brilliance of the Sun King (Apollonian motif reflected in East-West axis of the plan)
- passive appreciation of grand spectacles
- —“The sequence of the development of the gardens at Versailles is intimately related to the emerging power of the King [Louis XIV], his concept of monarchy, and his love affairs.”13
- —Louis XIV admitted: “In my heart I prefer fame above all else, even life itself. . . . Love of glory has the same subtleties as the most tender passions.”14
- means to confine and control a restive and potentially bothersome aristocracy
- —“To keep all these lords and ladies from being bored into regicide, artists of every kind were engaged to arrange amusements.”15
AMBIANCE
- Human-centered; dazzling play of light, hydraulic wonders in spouting fountains
- —“the form’s vast claim to have been true forever as the law of a universe in which nothing appears to change and there was nothing before this except defects of Nature a waste of marshes a lake a chaos of birds and wild things a river making its undirected way.”16
UNDERLYING PRINCIPLES
- Innovative, angular
- Severe symmetry, effusive fountains, ostentation, baroque convolutions, conscious contrivance, extravagant possessiveness, commanding attention, awe-inspiring
—“[T]he most extraordinary example of man imposing himself on nature, changing, shaping, adapting, altering the environment to his will, at whatever cost.”17
East/West Aesthetics: Musical Composition and Performance
Japan’s late Ashikaga to Early Edo Periods
WHAT
- Shika no Tone, “The Sound of Deer Calling to One Another” (the only shakuhachi piece included in Japanese junior high school music education classes)
WHO
- Kurosawa Kinko (1710–1771) founder of the Kinko school, who received a transmission from Buddhist priest Ikkeishi
HOW
- Most famous shakuhachi (vertical bamboo flute) piece, which can be played as a solo but often is performed as a duet, representing two deer calling to each other
- Technically demanding, but also allows for individual expression
- Five part piece: 1) Mura-Iki (octave rising) technique, 2) development of four climactic melodies, 3) intensification of emotion with reintroduction of original melody, 4) serene continuation of melody, 5) traditional “rushing to the end.”18
WHY
- In the seventeenth century the shakuhachi became associated with peripatetic kumuso or “straw-mat priests,” referred to as “priests of nothingness.”19
- Peforming on the flute was considered a form of Zen practice
AMBIANCE
- Emotional, intense, surprising turns, pregnant pauses, calm ending; evoking moods of loneliness and isolation
—“Within its lonesomeness and liveliness, the music depicts the world seikan or the serene contemplation.”20
—What begins as a description of a deer calling for its mate ends on a transcendent note: “it is as if, rather than viewing deer, the focus is changed to that of the scenery deep in the mountains where the leaves on the trees have turned red and yellow.”21
UNDERLYING PRINCIPLES
- Less is more
—“No matter how large or small an ensemble may be, the tone color of the instruments combined is such that the sounds do not ‘melt’ into a single experience . . . . Another important feature of Japanese traditional music is the general lack of interest in the type of vertical sound units known in the West as chords or harmony. . . . there is a general goal of creating the maximum effect with a minimum of material. . . the artistry of ‘less action—more meaning.’ The challenge is to the flexibility of the listener, not the composer or performer.”22
France’s Late Baroque to Early Rococo Periods
WHAT
- Concerts Royaux, Royal Concert Series, Pièces à deux clavecins, (Pieces for two Harpsichords)
WHO
- François Couperin (1668–1733) “organiste du Roi” and later “ordinaire de la musique de la chambre du Roi” to Louis XIV, heavily influenced by Italian style
HOW
- Two harpsichords engaged in a binary form of “question-and-answer”
- Allows for individualization, given requisite self-discipline, maximizing qualities of the instrument: “plucked attack,” “transparency,” “contrast,” “vibrant richness”
—“Tense dissonances and elaborate decorations suddenly give place to moments of an apparent simplicity that hardly any other composer could match.”23
WHY
- Favorite pieces of Louis XIV featured at weekly Sunday performances
—Couprin’s music “dissipated the royal melancholy”24 amid political and military challenges (such as the fiercely fought War of Spanish Succession)
AMBIANCE
- Lush and languorous notes flow mellifluously from the paired keyboards, with a stately undertone; carefully crafted pieces that do not disappoint our expectations of rational order amid tonal complexity
—“The voluptuous Allemande à deux Clavecins is the only one of Couperin’s surviving works in which each harpsichord plays independent left-and right-hand parts. The resulting sonority is impressively rich.”25
UNDERLYING PRINCIPLES
- Everything in excess
—Couperin’s “art crystallizes the miniature world of the Rococo and the attributes of Gallic genius—wit, refinement, pointed rhythm and scintillating ornament, clarity, and precision. This music is ‘French without tears.’ Its goal . . . : to charm, to delight, to entertain. . . . Listening to these supremely civilized measures, one understands Debussy’s remark: ‘French music aims first of all to give pleasure. Couperin, Rameau—these are true Frenchmen.’”26
NOTES
1. I wish to thank my colleague at SDSU, Professor M. C. Madhavan, for his enthusiastic involvement in the continuing evolution of the course concept and its text.
2. Numerous examples of the linkage between science and aesthetics can be found in the words of scientists themselves. For example, scientist/philosopher Werner Heisenberg (1901–1976), winner of the 1932 Nobel Prize in Physics, quotes Johannes Kepler (1571–1630): “Geometria est achetypus pulchritudinis mundi,” which he renders as “Mathematics is the archetype of the beauty of the world.” Heisenberg then notes “in exact science, no less than in the arts, [beauty] . . . is the most important source of illumination and clarity,” from “Science and Beauty,” in Quantum Questions: Mystical Writings of the World’s Great Physicists, edited by Ken Wilbur (Boston: Shambhala, 1985), 67, 68. Writing about physicist Andrew Strominger’s String Theory, K. C. Cole observes: “many of the greatest minds in physics are convinced of its ultimate truth—in large part because of its mathematical beauty. In the history of science, beauty has proved itself a reliable guide to truth. . . . Mostly what guides Strominger is a sense of aesthetics,” from “A Career Boldly Tied by Strings,” Los Angeles Times, 4 February 1997, sec. A16.
See also David Gelernter, Professor of Computer Science at Yale University, Machine Beauty: Elegance and the Heart of Technology (New York: Basic Books, 1998), which includes a chapter titled “The Aesthetics of Computer Science,” and John D. Barrow, The Universe and the Teacup: The Mathematics of Truth and Beauty (New York: Harcourt Brace, 1998).
3. Seiko Goto, The Japanese Garden: Gateway to the Human Spirit (New York: Peter Lang, 2003), 130.
4. Lunar-oriented aspects include a moon-viewing platform, moon-shaped architectural motifs, “the Basin for the Floating Moon,” “the Moon-Viewing Bridge,” “the Moon Viewing Window,” “the Tower of the Moon Wave,” and “walking moon” boat.
5. Goto, Japanese Garden, 134.
6. Shin’ichi Hisamatsu, Zen and the Fine Arts, translated by Gishin Tokiwa (Tokyo: Kodansha international Ltd., 1971), 83.
7. Bruno Taut (1936) quoted by Peregrine Hodson, “Katsura,” in Living in a Dream: Great Residences of the World (New York: Simon & Schuster, 1993), 151.
8. Walter Gropius quoted by Hodson, Living in a Dream, 151.
9. Hisamatsu, Zen and the Fine Arts, 89.
10. “Seven Characteristics of Zen Aesthetics” in Hisamatsu, Zen and the Fine Arts, 28–37.
11. Hisamatsu, Zen and the Fine Arts, 85.
12. Will Durant and Ariel Durant, The Story of Civilization: 8, The Age of Louis XIV, A History of European Civilization in the Period of Pascal, Molière, Cromwell, Milton, Peter the Great, Newton, and Spinoza: 1648–1715 (New York: MJF Books, 1963), 92.
13. William Howard Adams, The French Garden 1500–1800 (New York: George Braziller, 1979), 84.
14. Louis XIV, Mémoires, as quoted in The New Encyclopaedia Britannica Macropaedia, 11, fifteenth ed. (Chicago: Encyclopaedia Britannica, 1975), 122a.
15. Durant and Durant, Story of Civilization, 32.
16. W. S. Merwin, “The Garden of Versailles: A Poet Reflects Upon the Crown Jewel of French Landscape Art that André Le Nôtre Devised for Louis XIV,” The New York Times Magazine, 18 September 1994.
17. Roger Phillips and Nicky Foy, A Photographic Garden History (New York: Random House, 1995), 78.
18. John Singer, The International Shakuhachi Society—Shika no Tone (Kinko Ryu); available from http://www.komuso.com/pieces/Shika_no_Tone_ (Kinko_Ryu).html, page 1; accessed 26 October 2003.
19. “Shakuhachi,” Japan: An Illustrated Encyclopedia, 2 (Tokyo: Kodansha Ltd., 1993), 1355.
20. Katsuya Yokoyama, International Shakuhachi Society, 6.
21. John Singer, International Shakuhachi Society, 1.
22. “Music, traditional,” Japan: An Illustrated Encyclopedia, 2, 1023–4.
23. Norman Lloyd, The Golden Encyclopedia of Music (New York: Golden Press, 1968), 127.
24. Lloyd, Golden Encyclopedia of Music, 127.
25. Kenneth Slowik, notes to F. Couperin, Concerts Royaux Pièces a Deux Clavecins, Smithsonian Chamber Players, Deutsche Harmonia Mundi 05472 77327 2, 7.
26. Joseph Machlis, The Enjoyment of Music: An Introduction to Perceptive Listening, rev. ed. (New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 1963), 460.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Adams, William Howard. The French Garden 1500–1800. New York: George Braziller, 1979.
Couperin, F. Concerts Royaux Pièces a Deux Clavecins, Smithsonian Chamber Players, Deutsche Harmonia Mundi 05472 77327 2.
Durant, Will and Ariel Durant. The Story of Civilization: 8, The Age of Louis XIV, A History of European Civilization in the Period of Pascal, Molière, Cromwell, Milton, Peter the Great, Newton, and Spinoza: 1648–1715. New York: MJF Books, 1963.
Goto, Seiko. The Japanese Garden: Gateway to the Human Spirit. New York: Peter Lang, 2003.
Hisamatsu, Shin’ichi. Zen and the Fine Arts, trans. Gishin Tokiwa. Tokyo: Kodansha International Ltd., 1971.
The International Shakuhachi Society—Shika no Tone (Kinko Ryu) http://www.komuso.com/pieces/Shika_no_Tone_(Kinko_Ryu).html, accessed 26 October 2003.
Japan: An Illustrated Encyclopedia, 2 (Tokyo: Kodansha Ltd., 1993).
Living in a Dream: Great Residences of the World. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1993.
Lloyd, Norman. The Golden Encyclopedia of Music. New York: Golden Press, 1968.
Machlis, Joseph. The Enjoyment of Music: An Introduction to Perceptive Listening, rev. ed. New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 1963.
Merwin, W. S. “The Garden of Versailles: A Poet Reflects Upon the Crown Jewel of French Landscape Art that André Le Nôtre Devised for Louis XIV,” The New York Times Magazine, 18 September 1994.
Phillips, Roger and Nicky Foy. A Photographic Garden History. New York: Random House, 1995.
Wilbur, Ken, ed., Quantum Questions: Mystical Writings of the World’s Great Physicists. Boston: Shambhala, 1985.